Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and Power Equipment, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
3 Global Energy Interconnection Development and Cooperation Organization, Beijing 100031, China
4 Systems Engineering Research Institute, Beijing 100094, China
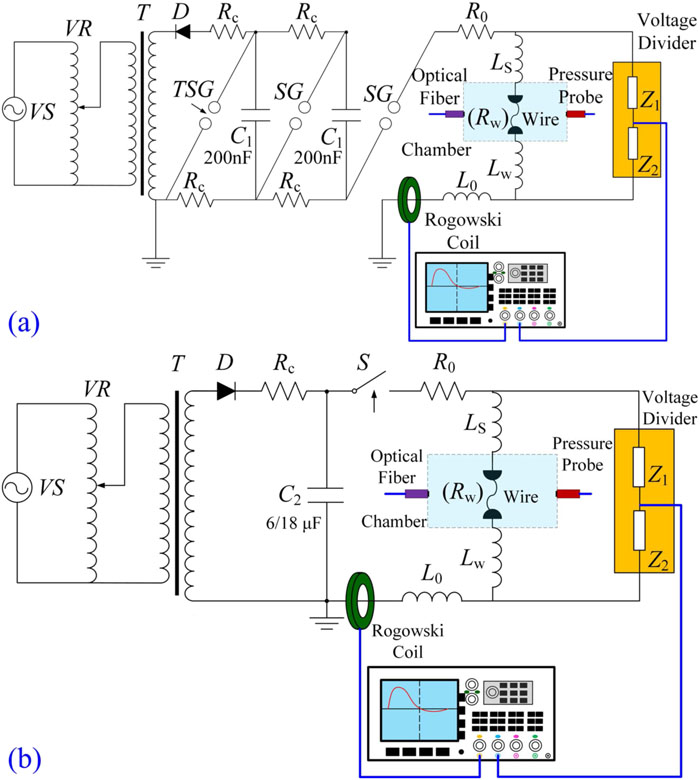
Underwater shock waves generated by pulsed electrical discharges are an effective, economical, and environmentally friendly means of stimulating reservoirs, and this technology has received much attention and intensive research in the past few years. This paper reviews the main results of recent work on underwater electrical wire explosion (UEWE) for reservoir stimulation. A platform is developed for microsecond single-wire explosions in water, and diagnostics based on a voltage probe, current coil, pressure probe, photodiode, and spectrometer are used to characterize the UEWE process and accompanying shock waves. First, the UEWE characteristics under different discharge types are studied and general principles are clarified. Second, the shock-wave generation mechanism is investigated experimentally by interrupting the electrical energy injection into the wire at different stages of the wire-explosion process. It is found that the vaporization process is vital for the formation of shock waves, whereas the energy deposited after voltage collapse has only a limited effect. Furthermore, the relationships between the electrical-circuit and shock-wave parameters are investigated, and an empirical approach is developed for estimating the shock-wave parameters. Third, how the wire material and water state affect the wire-explosion process is studied. To adjust the shock-wave parameters, a promising method concerning energetic material load is proposed and tested. Finally, the fracturing effect of the pulsed-discharge shock waves is discussed, as briefly are some of the difficulties associated with UEWE-based reservoir stimulation.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2020, 5(4): 047201
1 苏州大学物理与光电·能源学部, 江苏 苏州 215006
2 江苏省现代光学技术重点实验室, 江苏 苏州 215006
为满足光谱仪微型化、便携化的要求,并克服基于台式电脑处理系统的光谱仪在户外使用不便的缺点,研制了一种基于Android系统的微型光谱仪。介绍了仪器研制过程中的光学、机械、电子学以及应用软件(APP)的设计。光学系统利用平场全息凹面光栅简化系统光路结构,机械结构使用3D打印技术一体化成型。选用线阵CCD(TCD1304DG)作为光电探测器,用全新的STC15系列嵌入式微控制单元(MCU)为控制核心,采用Android USB(系统通用串行总线)接口用于通信,完成了Android系统下高分辨率光谱数据采集系统的设计。编制APP用于实时处理光谱数据。运用电子快门技术,实现了Android设备对CCD积分时间的实时在线可调,满足了便携式光谱仪在不同环境下的工作要求。设计方案以Android系统作为数据处理平台,代替了传统台式电脑处理系统,体现了较好的便携性优势。
光谱学 微型光谱仪 线阵CCD 积分时间 Android USB通信 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(6): 063001
1 西安交通大学 电力设备电气绝缘国家重点实验室, 西安 710049
2 西安贯通能源科技有限公司, 西安 710068
介绍了复合电热化学法产生冲击波的机理和冲击波改善储层物性的机制; 给出了脉冲大电流引爆含能材料弹丸的结构和典型的放电参数,开展了冲击波致裂储层的实验研究; 检测了样品在冲击作用下的动态应变及影响储层解吸附特性的关键参数(包括孔隙度、渗透率、抗拉、抗压强度等),并在实验前后进行了测量和对比。研究表明,电热化学法产生的冲击波可在圆柱形砂岩样品上产生幅值为1000με~1500με的应变量,使砂岩出现了宏观裂缝; 样品平均孔隙度由15.24%增至15.62%,平均渗透率由1.749 09×10-3 μm2增至2.467 08×10-3 μm2; 抗压、抗拉和抗剪强度均下降了约30%。
脉冲放电 含能材料 等离子体引爆 冲击波 物性参数 储层改造 pulsed discharge energetic materials plasma-ignited explosion shock wave petrophysical parameters reservoir transformation 强激光与粒子束
2016, 28(4): 049001





